Hermes v1
The missing twin
Highlights
Overview
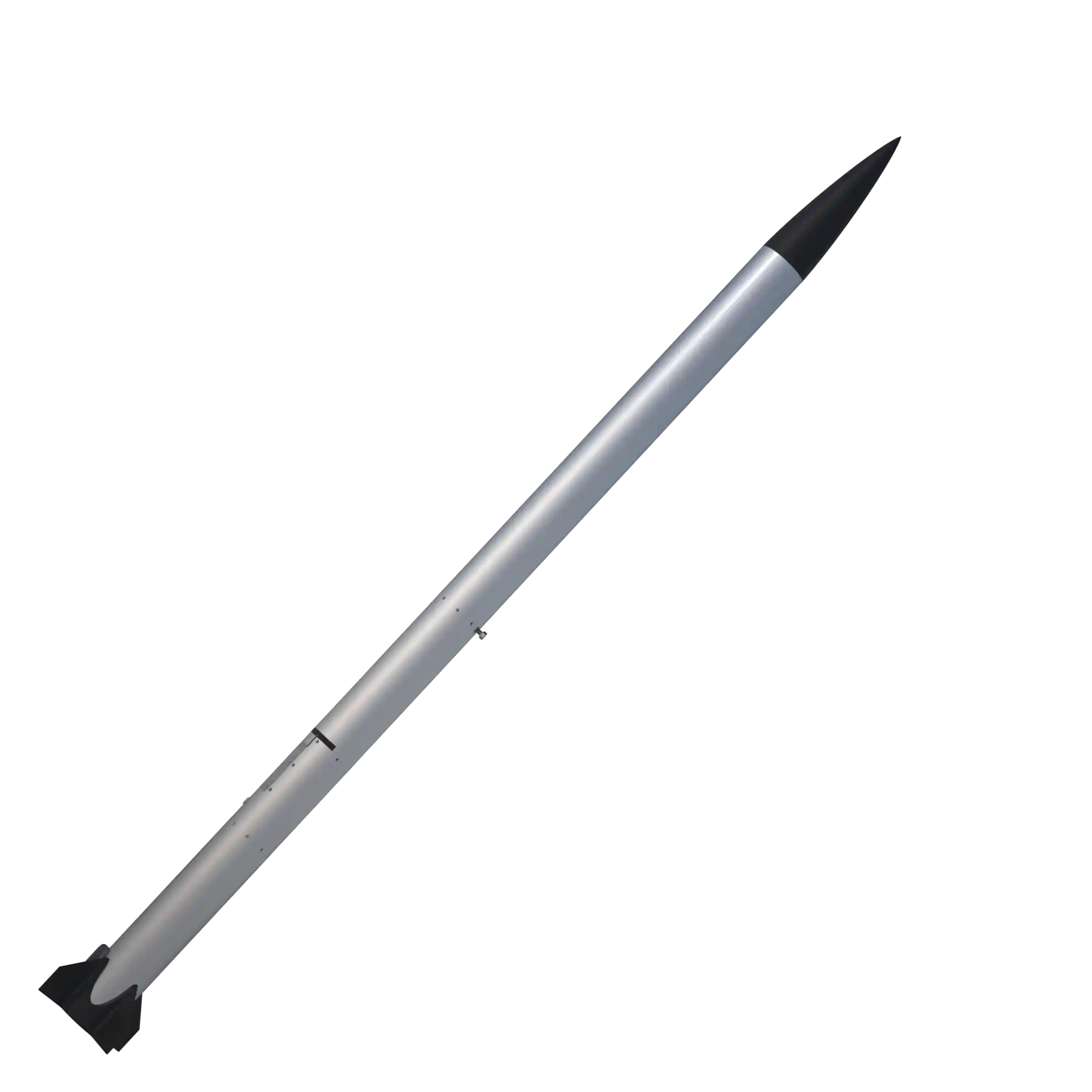
Hermes V1 is the evolution of the first hermes in order to test the new expulsion system. It is lighter and with a monocoque fuselage made by a single tube in aluminum.
It is launched after only 3 months of work maintaining most of the design similar to the previous one aside the rogallo wing that is substituted by a most conventional cruciform parachute. The rocket was produced in 2 identical prototypes, one launched successfully at Roccaraso (AQ) and however resulted in a ballistic flight again. The second launch scrubbed due to bad weather and a bug in the flight computer


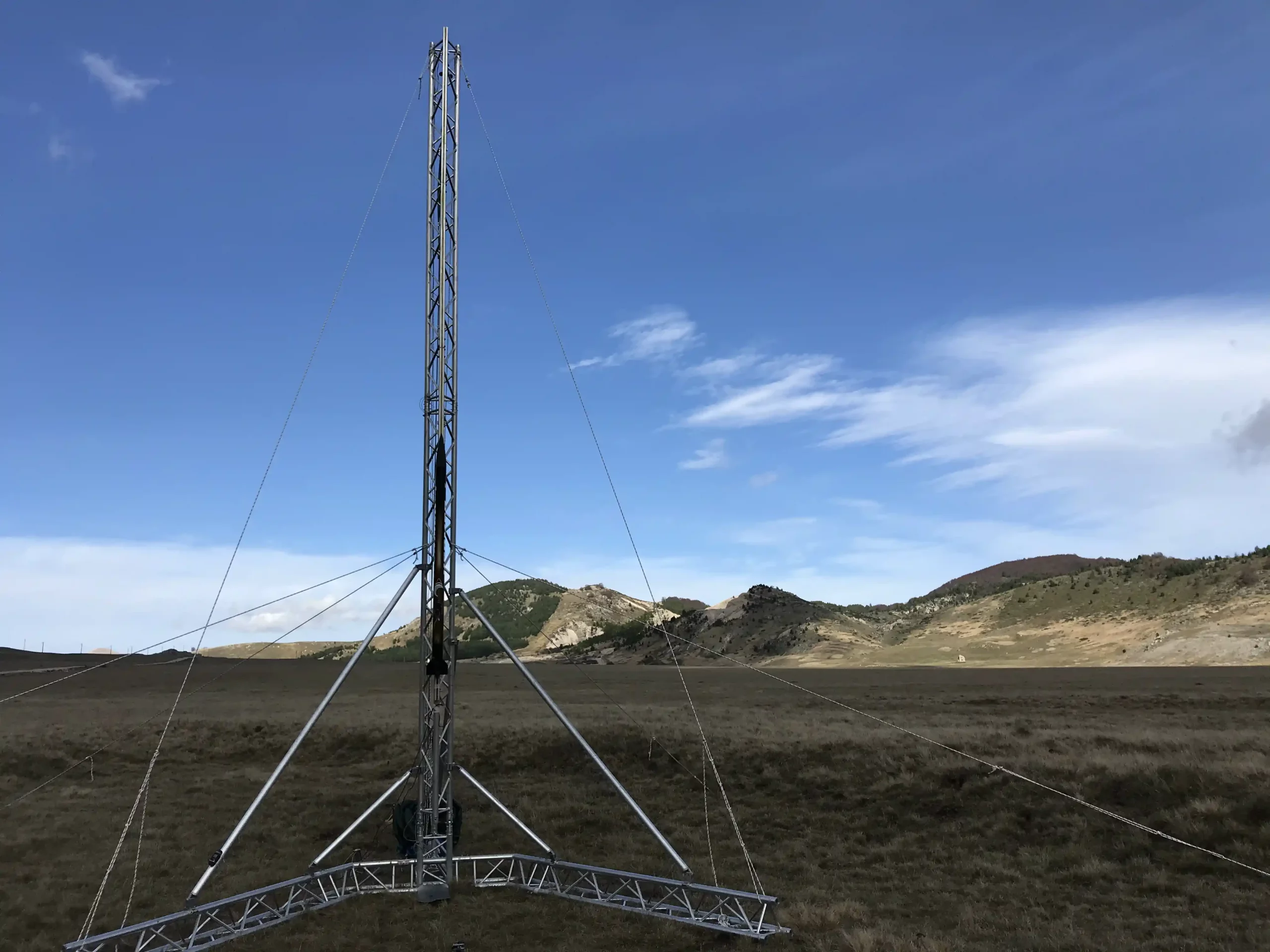
Roccaraso Flight
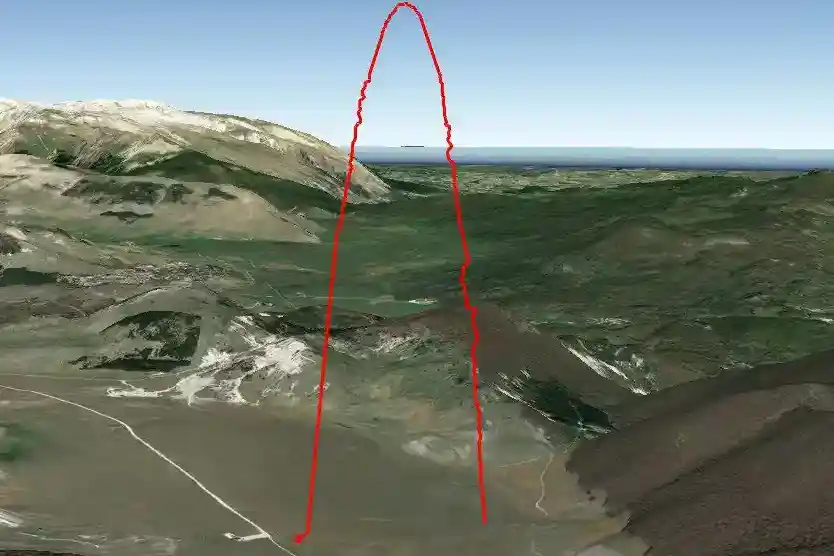
The launch took place on 15th of November 2021 at Piano dell’Aremogna Roccaraso. The rocket lifts-off perfectly after the ignition of the motor and goes straight up almost without rolling thanks to the 3D printed fins. The apogee was detected correctly at 1315 m AGL but the nose cone separation didn’t occur despite the servomotor of the expulsion valve being actuated as heard in the on board video. The rocket landed ballistically in the middle of the plain suffering severe damage but not catastrophic, thanks to that it was possible to recover the video from the onboard camera.

specs
Aerotech
K550


Structure
The main focus on the structure is to reduce the lift-off weight with respect to Hermes V0. For this reason it adopted a monocoque in aluminum for the fuselage and a nose cone and fins optimized in nylon loaded carbon 3D printed. The shape of the fins and of the nose cone is optimized to be more efficient as possible: for the nose cone is chosen a von karman ogive. The inner structure is composed by 3 threaded bars attached to the recovery bulkhead that hold all the other flanges 3D printed in PLA for electronics components. The motor is retained in the same way of Hermes V0 with two aluminum flanges.
Electronics
The Flight computer is the same as the previous Hermes because it works perfectly with minor bugs and there isn’t enough time to develop a new one

Expulsion
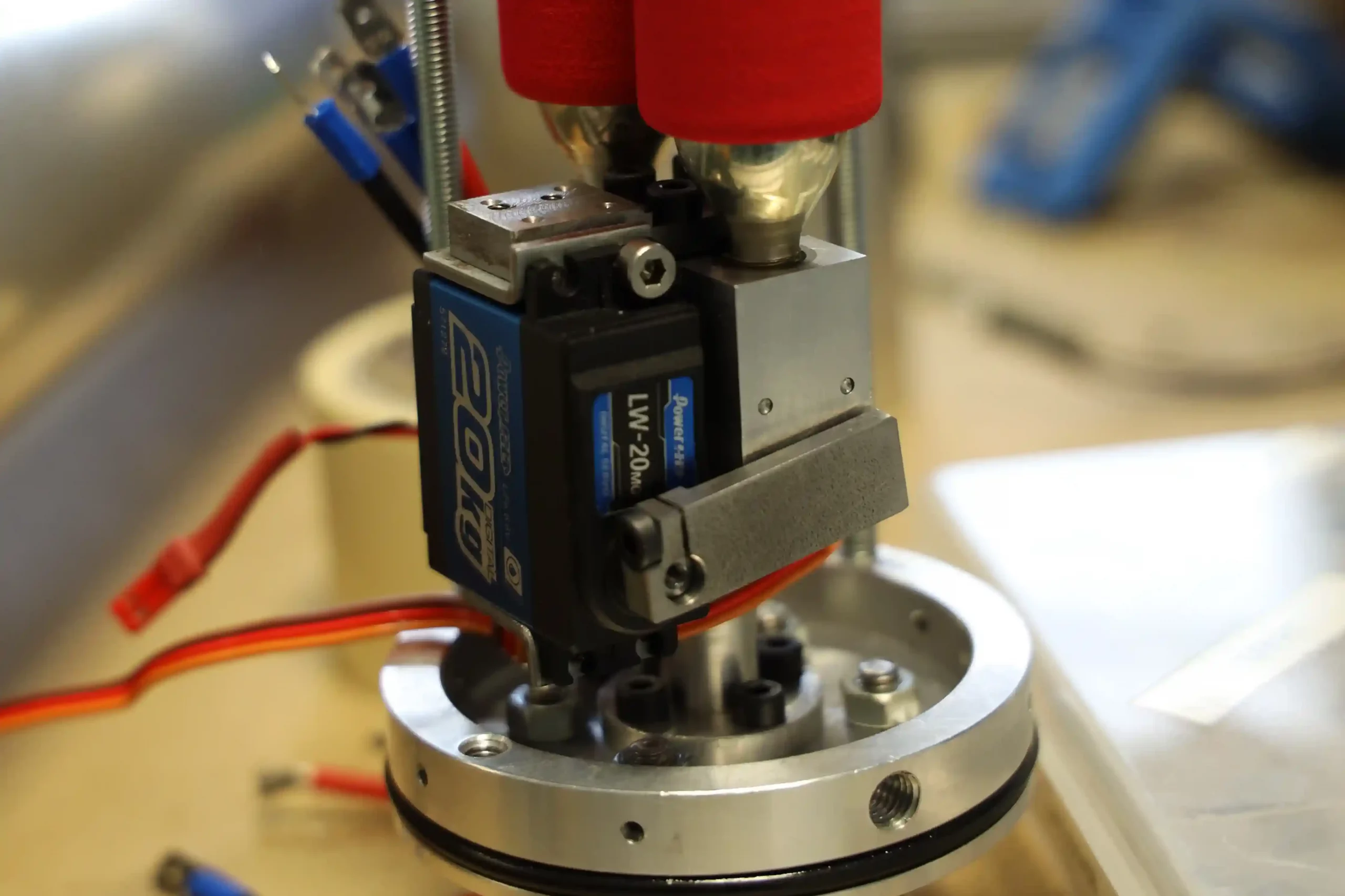
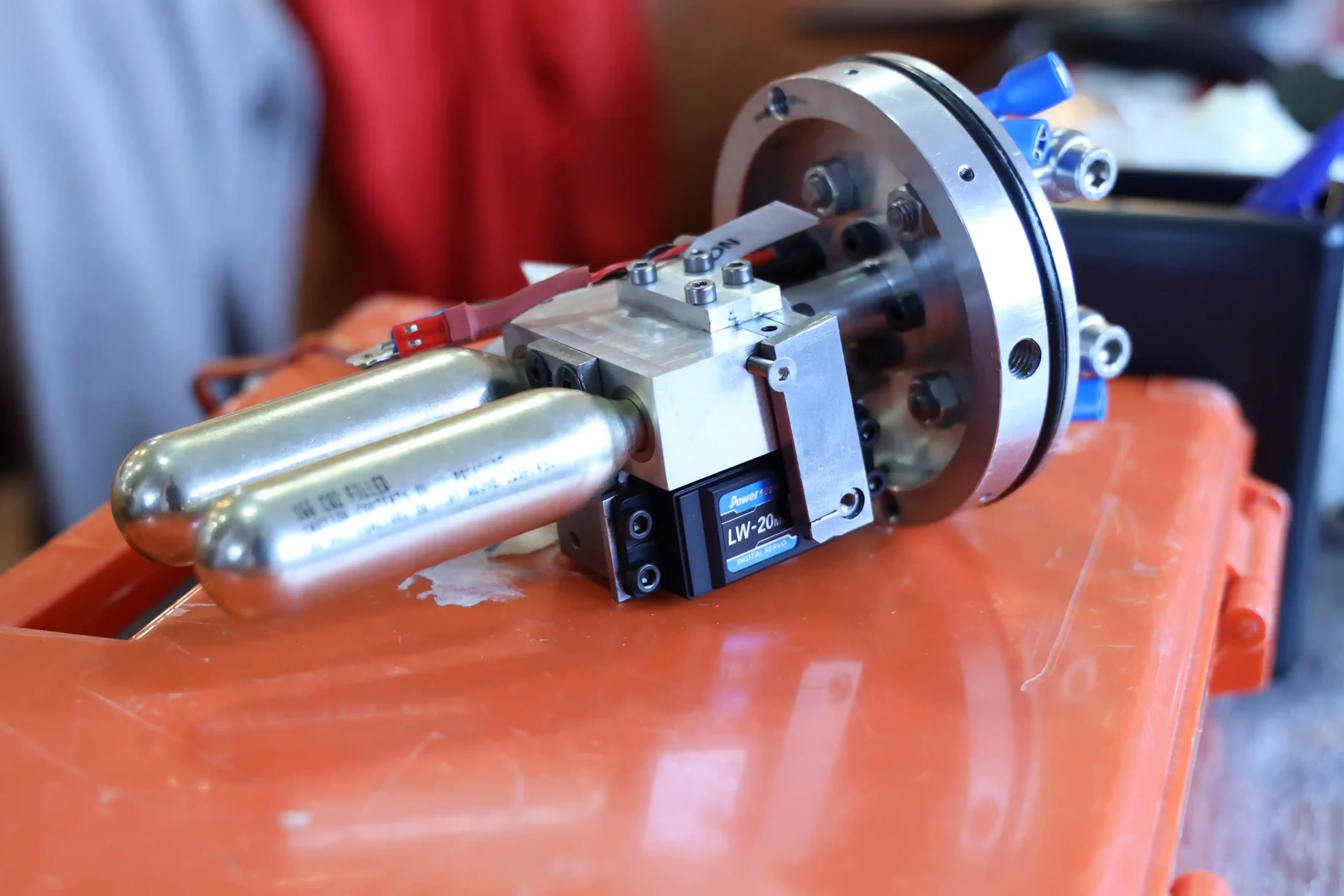
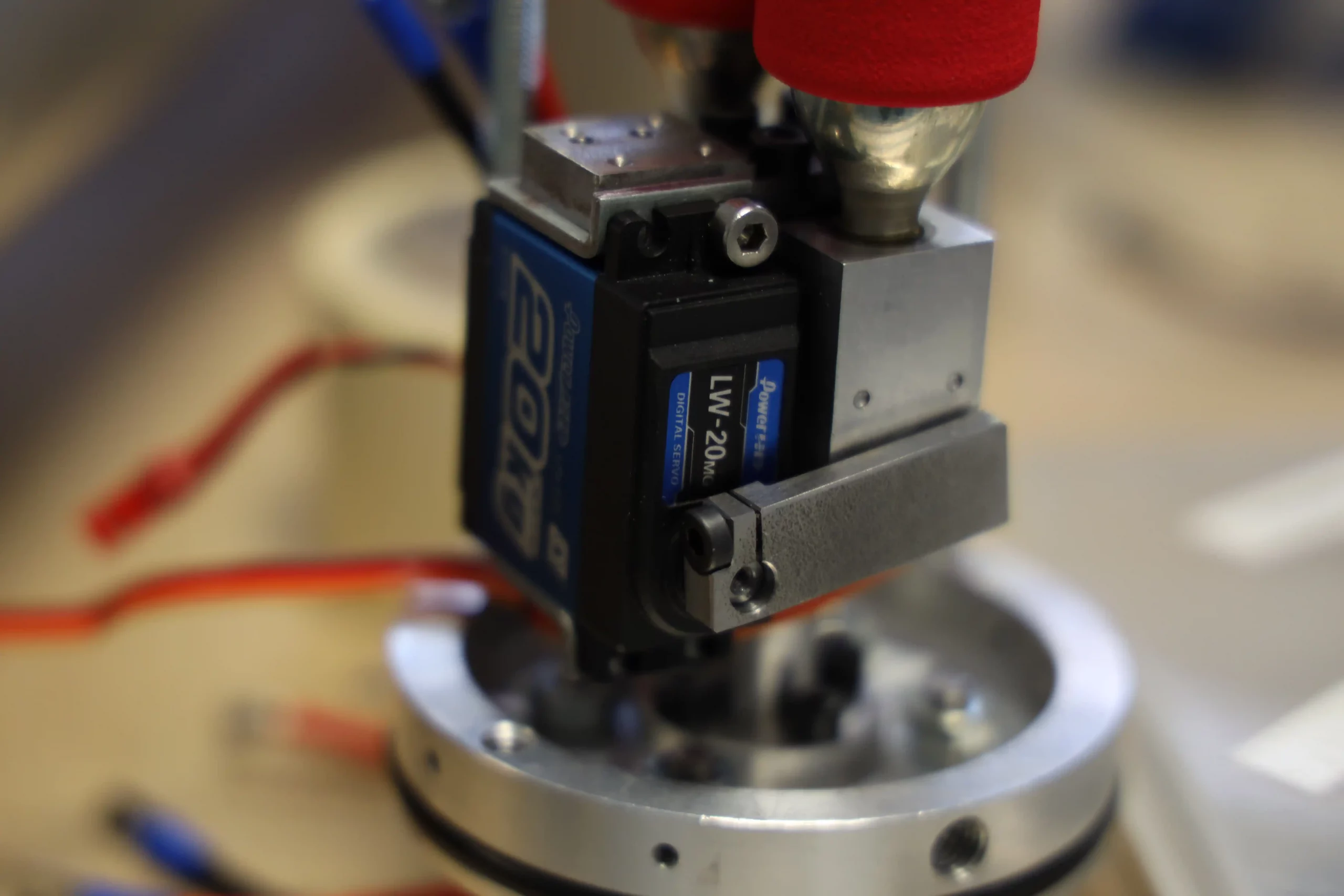
The expulsion system is completely different with respect to the one of Hermes V0 that has several design problems. The new system developed in only two months is a pneumatic valve actuated by a servo motor attached to the recovery bulkhead. The valve releases the gas contained in two canisters of C02 (very flexible to mount different canister sizes) in the sealed with o-rings recovery bay and in this way the nose cone is ejected. The valve is very compact and lightweight and can be adapted
Recovery
The recovery system is composed of two stage one drogue chute open at apogee and a more conventional main cruciform parachute open at 450 meter from ground. The staging of the system is performed using a NiCr wire cutter actuated by the flight computer. The main parachute is the same as the R1-X rocket and also the one used by Lynx.
